
Sugar Damage
Diet-wise, carbohydrate-heavy and sugary foods contribute the most sugar that is later absorbed by the body. This sugar damage, which may also be aggravated by daily life stressors, can result in:
-

Gain Weight
-

Gastrointestinal Problems
-

Skin Glycation
-

Other Health Risks


If so, we’ll just cut out carbohydrates then!
Low-carb diets may lead to short-term weight loss, but such diets are not without their drawbacks. Severe carb restriction may result is side effects.
Don’t Forget about Sugar
Excessive sugar intake can lead to weight gain, even with regular exercise.
High-sugar diets can cause leptin resistance. Leptin is the hormone that tells your brain when you're full, reducing your appetite. When your body becomes resistant to leptin, it can lead to overeating and unwanted weight gain.


-

Unhealthy diet
Consuming excess carbohydrates and simple sugars can lead to bloating and water retention. A diet lacking in fiber can slow down digestion, resulting in poor gut mobility and constipation. Adequate fiber intake is essential to keep the digestive system functioning smoothly.
-

Antibiotic use
While antibiotics effectively treat bacterial infections, they can also disrupt the balance of good gut bacteria, leading to digestive issues such as diarrhea. Harmful bacteria like Clostridium difficile may overgrow, causing further problems. Probiotics can help reduce the risk of antibiotic-related diarrhea and assist in managing other gut issues, like chronic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome.
-

Stress
Stress can negatively impact gut health by increasing sensitivity, reducing blood flow, and disrupting gut flora balance. Incorporating probiotics and prebiotics can help restore healthy gut bacteria, promote balance, and support digestion.

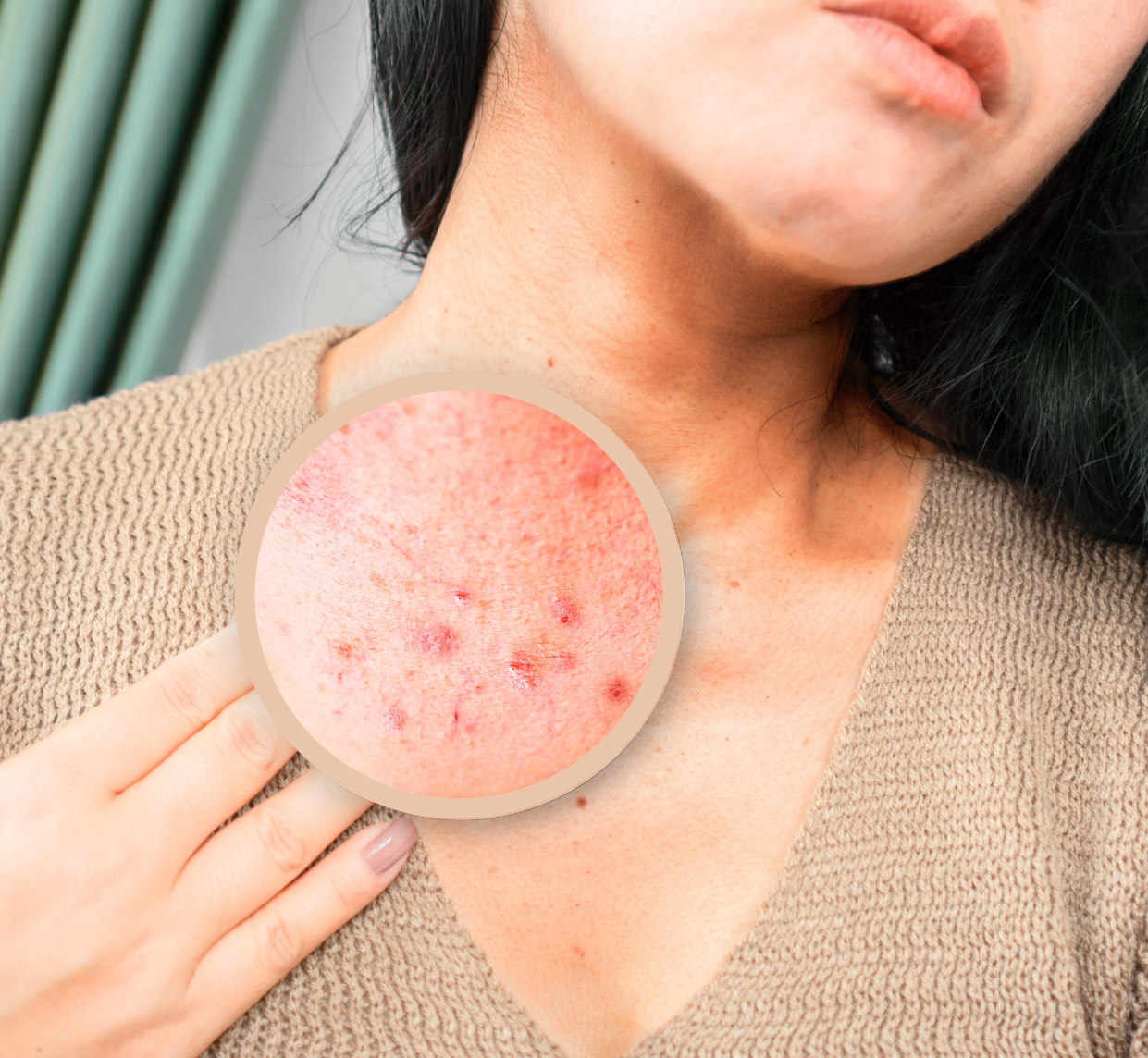
Sugary foods can harm your skin too.
Excess sugar can damage collagen, the protein responsible for keeping your skin firm, elastic, and hydrated. When collagen binds with sugar, it forms advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are irreversible. Over time, this leads to skin aging, reduced elasticity, and a stiffened appearance.


-

Lethargy or fatigue
Consuming too many carbohydrates spikes blood sugar levels, providing short bursts of energy. However, this is often followed by feelings of fatigue and exhaustion.
-

Constant thirst
Eating high-carb foods raises blood sugar levels, making you feel thirstier as your body tries to rehydrate the bloodstream.
-

Headaches
A carb-heavy meal can cause a sudden rise in blood sugar, which may lead to headaches.
-

Poor digestion
Overconsumption of carbs can result in bloating, abdominal cramps, and heartburn due to the body's difficulty in metabolizing them effectively.
-

Mood swings
After a sugar rush, you may experience an emotional crash, leaving you feeling irritable. Excessive carbs can also imbalance brain chemicals, increasing the likelihood of depression and anxiety.
-

Sugar cravings
When sugar is consumed, it triggers the release of dopamine, the "feel-good" hormone, causing the body to crave more sugar for the same reward.
-

Feeling hungry easily
Refined carbs are stripped of nutrients and fiber, turning them into empty calories that are quickly digested, making you feel hungry more often.
-

Difficulty losing weight
Excess glucose is converted into fat and stored in the body, making weight loss more challenging.
-

High blood cholesterol
Carb-heavy diets are linked to lower levels of HDL (good) cholesterol and higher levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
-

High blood glucose
Overeating carbs like white rice or pasta can cause blood sugar levels to spike, which is especially problematic for individuals with diabetes.




















